
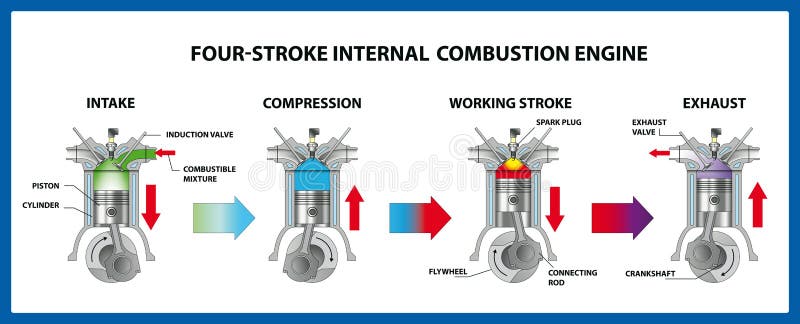
For a petrol engine, the air-fuel ratio used is 8:1 to 12:1 The fuel injector introduces the appropriate amount of fuel so that the requires air-fuel ratio is achieved. The inlet valve is open during this stroke to pull in fresh air-fuel mixture from the intake manifold. Intake Stroke : The piston moves from the TDC to the BDC in this stroke.Now that you are familiar with some of the components of the engine we can get into the Otto Cycle which is responsible for cars moving.Ĥ-Stroke Engine By Zephyris (Own work), via Wikimedia Commons Fuel Injector : This sprays fuel into the intake manifold so that a good air-fuel ratio is achieved before the air-fuel mixture enters the cylinder.The precise timing for release of the spark is achieved using the ignition system Spark Plug : This component provides a spark at the end of the compression stroke to ignite the air-fuel mixture and trigger combustion.In the 4-Stroke engine, there is one power stroke per two revolutions of the crankshaft. The crankshaft in turn connects to the flywheel. Crankshaft : The crankshaft is connected to the pistons of each cylinder in the engine and is rotated by the torque provided to it by the pistons through the connecting rod.Connecting rod : This connects the piston to the crankshaft.It also prevents oil from the sump lubricating the crankshaft from getting pulled into the cylinder and getting combusted Piston rings : These provide a sliding seal to prevent leakage of the air-fuel mixture or combustion products within the cylinder.The upper extreme point that the piston reaches within the cylinder is the Top Dead Center (TDC) while the lower extreme is the Bottom Dead Center (BDC) This vertical motion is converted to rotational motion in order to move the car. Piston : The piston moves up and down within the cylinder.The adjacent picture shows Dual Overhead Cams rotating above the valves. These can be used along with rocker arms, pushrods (Over Head Valve systems) or by themselves in the case of Overhead cams (single or dual) to regulate the valves. Camshaft : The opening and closing of the valves are regulated by the camshaft which is basically a shaft having one or more cams(projections) attached to it.

The adjacent picture shows the two valves at the top of the cylinder. The inlet valve lets fresh fuel mixture into the cylinder and the exhaust valve allows the exhaust gases to leave the system after combustion.

(Uploaded by Frack), via Wikimedia Commons Engine Cylinder Created by Wapcaplet in Blender.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
